Athena Skin Hair & Dental Clinic
Scar Removal
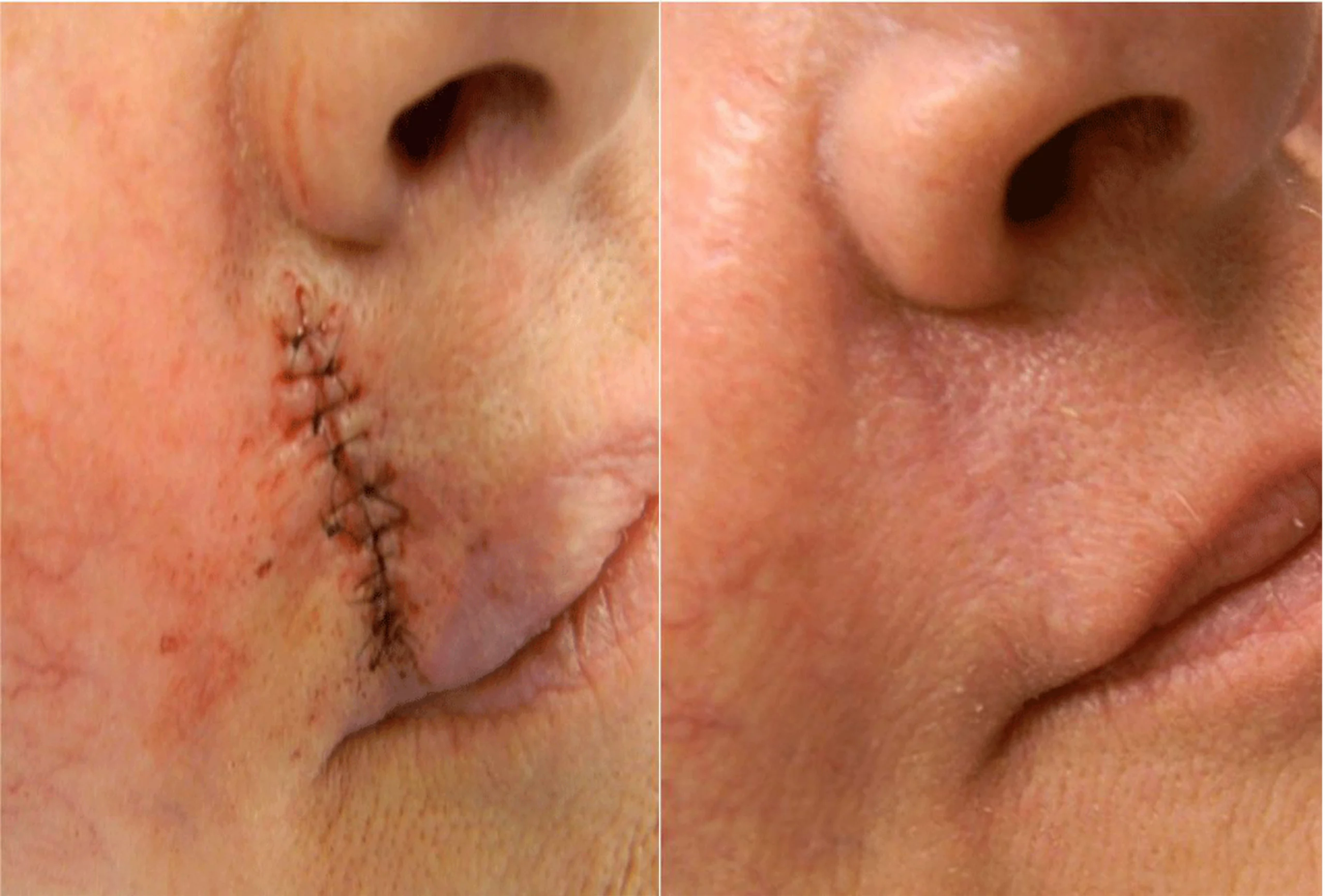
What is Scar Removal
Symptoms of Scarring
Scarring symptoms vary depending on the type of scar. Common symptoms include:
-
Raised or depressed skin areas
-
Discoloration (red, brown, or white patches)
-
Thickened or stiff skin
-
Itchiness or tenderness around the scar
-
Pain or discomfort in severe cases
Types of scars:
-
Hypertrophic scars – Raised and red scars that remain within the wound area.
-
Keloid scars – Overgrown tissue that extends beyond the original injury.
-
Atrophic scars – Depressed scars, often from acne or chickenpox.
-
Contracture scars – Tight, thick scars that can restrict movement, common with burns.
Causes of Scarring
Scars form when the skin heals from damage, but the severity of scarring depends on:
-
Injury type (cuts, burns, surgery, acne, infections)
-
Genetic factors (some individuals are more prone to keloids and hypertrophic scars)
-
Skin type (darker skin tones are more likely to develop prominent scars)
-
Depth and size of the wound (deeper wounds tend to scar more prominently)
-
Healing process (poor wound care, infections, or excessive tension on stitches can worsen scars)
Scar Removal Treatments
Several treatments are available to improve scar appearance, depending on the scar type and severity.
Non-Surgical Treatments
-
Topical Treatments – Creams, gels, and silicone sheets containing vitamin E, retinoids, or corticosteroids can help lighten and soften scars.
-
Laser Therapy – Reduces redness and flattens scars by targeting pigment and stimulating collagen production.
-
Chemical Peels – Removes damaged skin layers to improve texture and pigmentation.
-
Microdermabrasion & Dermabrasion – Exfoliates the skin to reduce scar depth and appearance.
-
Steroid Injections – Helps flatten and reduce inflammation in hypertrophic and keloid scars.
-
Microneedling – Stimulates collagen production, making scars less visible.
Surgical Procedures
-
Scar Revision Surgery – Removes scar tissue and closes the wound with minimal scarring techniques.
-
Skin Grafting – Used for larger scars, where healthy skin is transplanted to cover the affected area.
-
Cryotherapy – Freezing treatment for keloid scars, helping shrink them over time.
-
Subcision – Used for depressed scars, breaking fibrous tissues to lift the scarred skin.
Prevention of Scars
While some scarring is unavoidable, these steps can minimize their formation:
-
Proper Wound Care – Clean wounds, apply antibiotic ointment, and cover them with bandages.
-
Avoid Picking at Scabs – Let wounds heal naturally to prevent deep scars.
-
Use Sunscreen – Protect scars from UV rays to prevent darkening.
-
Massage the Scar Area – Helps break down scar tissue and improve flexibility.
-
Stay Hydrated and Maintain a Healthy Diet – Promotes faster healing and collagen production.
Recovery and Aftercare
Recovery time depends on the treatment type:
-
Topical treatments – Weeks to months of consistent use.
-
Laser therapy and chemical peels – Few days to weeks for healing.
-
Surgical procedures – Several weeks to months for full recovery.
